Dietician Shilpi Goel shares her perspective on why she thinks BMI to be just a ‘Blurred Miscalculated Index’, rather than an accurate measure of overall health.
Body mass index (BMI) is a standard health assessment tool in most healthcare facilities. The BMI was developed in 1832 by a Belgian mathematician named Lambert Adolphe Jacques Quetelet.
He developed the BMI scale to quickly estimate the degree of being overweight and obesity in a given population to help governments decide where to allocate health and financial resources.
The BMI scale is based on a mathematical formula that determines whether a person is of a “healthy” weight by dividing their weight in kilograms by their height squared in meters:
BMI = weight (kg) / height (m2)
Once BMI is calculated, it’s then compared to the BMI scale to determine whether you fall within the “normal” weight range.
BMI range Classification Risk of poor health less than 18.5 underweight high 18.5–24.9 normal weight low 25.0–29.9 overweight low to moderate 30.0–34.9 obese class I (moderately obese) high 35.0–39.9 obese class II (severely obese) very high 40 or greater obese class III (extremely obese) extremely high
According to this calculation, a healthcare professional may suggest health and lifestyle changes if you don’t fall within the “normal” weight category.
Though it has been used for decades as the go-to measurement for health based on body size, it has been widely criticized for its oversimplification of what being healthy really means.
Interestingly, Quetelet stated that BMI was not useful in studying single individuals but rather in giving a snapshot of a population’s overall health. Nevertheless, it’s widely used to measure individuals’ health.
While BMI may be a quick, affordable, and easily accessible way to screen a person’s health, the formula is better suited for information about general populations, when analysing BMI on the individual level, there are several other factors to consider that BMI does not take into account:
Recommended Story : Ayurvedic Diet: 10 Rules To Stick To For Disease Free Life
Limitations Of BMI Health Assessment Test:
1. Assumes all weight to be equal

Though 1 kilogram of muscle weighs the same as 1 kilogram of fat, muscle is denser and takes up less space compared to body fat. As a result, a person who has a lean body but high muscle mass may have a higher BMI on the scale.
However, two people of the same height and weight could look completely different. One may be a bodybuilder with high muscle mass, while the other may have higher fat mass.
If only BMI is considered, this could easily misclassify a person as “overweight” or “obese” despite their low fat mass. Therefore, it’s important to consider a person’s muscle, fat, and bone mass in addition to their weight.
2. Doesn’t takes into account the overall health condition of a person

BMI only answers “yes” or “no” regarding whether a person is of “normal” weight, without any context of their age, sex, genetics, lifestyle, medical history, or other factors.
Relying only on BMI may miss other important factors affecting health, such as cholesterol, blood sugar, heart rate, blood pressure, and inflammation levels. It might also overestimate or underestimate a person’s real health status as with age the body fat mass naturally increases and muscle mass naturally declines.
Inspite of varying body compositions of men and women— with men having more muscle mass and less fat mass than women — BMI uses the same calculation for all groups.
3. Does not measure body fat percentage
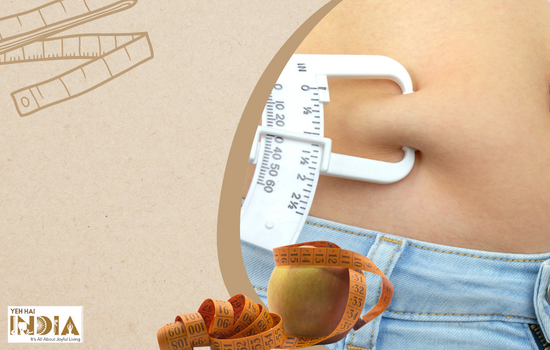
Body fat percentage (BFP) is the percent of your body that is fat tissue compared to your total body mass. One of the main issues with BMI is that it cannot account for the difference between muscle and fat.
Because muscle tissue is denser than fat, many athletes and bodybuilders are considered overweight according to BMI despite being in peak athletic health.
Body fat percentage will give a better assessment of health because the disease risk is more correlated with body fat rather than body weight.
4. May lead to weight bias

It’s expected that a medical professional uses their best judgment, meaning they would take the BMI result and consider their patient as a unique individual.
However, some health professionals use only BMI to measure a person’s health before providing medical recommendations, which can lead to weight bias and poor quality healthcare
Those with higher BMIs more often report that their doctors focus only on their BMI, even if their appointment is for an unrelated concern. Often, serious medical issues go unnoticed or are incorrectly seen as weight-related problems.
In fact, studies have shown that the higher a person’s BMI is, the less likely they are to attend regular health check-ups due to fear of being judged, distrust of the healthcare professional, or a previous negative experience. This can lead to late diagnoses, treatment, and care.
5. Does not measure body fat distribution

The specific location of fat is another important factor when considering overall health, and is a measure that BMI does not adjust for. Upper body fat around the midsection and visceral fat are more correlated to health complications, such as cardiovascular disease than lower body fat around the thighs and butt region.
6. Does not consider ethnicity

Despite the wide use of BMI among all adults, it may not accurately reflect the health of certain racial and ethnic populations.
Some other alternatives to determine health status
Despite the many flaws of BMI, it’s still used as a primary assessment tool because it’s convenient, cost-effective, and accessible in all healthcare settings.
However, there are alternatives to BMI that may be better indicators of a person’s health.
1. Waist circumference

A larger waist circumference — one greater than 35 inches (85 cm) in women or 40 inches (101.6 cm) in men — indicates greater body fat in the abdominal area, which is associated with a higher risk of chronic disease.
2. Waist-to-hip ratio

A high ratio (greater than 0.80 in women or greater than 0.95 in men) indicates higher fat stores in the stomach area and is linked to a greater risk of heart and chronic disease.
A low ratio (lower than or equal to 0.80 in women or lower than or equal to 0.95 in men) suggests higher hip fat storage, which is associated with better health.
3. Body fat percentage

As discussed above body fat percentage is the relative amount of body fat a person has and it distinguishes between fat mass and fat-free mass and is a more accurate representation of health risk than BMI.
It is normally measured with skinfold callipers, bioelectrical impedance, or most accurately through a DXA X-ray Scan.
4. Lab tests
Lab tests are various blood and vital sign measurements that can indicate chronic disease risk (e.g., blood pressure, heart rate, cholesterol, blood glucose levels, inflammation).
These tests provide a more detailed review of a person’s metabolic health and don’t rely only on body fat as a measurement of health.
Summary:

Regardless of the assessment tool used, it’s important for healthcare professionals to not rely on one test alone. For example, a healthcare professional may measure a person’s BMI and waist circumference, and if concern arises, a blood test may follow.
It’s important to treat each patient individually to determine what health means to them — physically, mentally, emotionally, and spiritually.
“BMI exaggerates thinness in short people and fatness in tall people so think of BMI like a puzzle piece: it’s a part of your whole health picture. It can be useful as a starting point, it should not be the only measurement of your health.”
- Shilpi Goel – Nutritionist, Dietitian and Founder of Nutrishilp.
Feel free to connect with Team Nutrishilp for any health related issues. Just dial or whats app @ 7581921000 or contact@nutrishilp.com.
Also Read : Famous Top 10 Nutritionists (Best Dietician) to Follow in India










